An engine is a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy.
Car engines are the heart and soul of vehicles, providing the power needed to propel them down the road. But among the types used in production are different fuels, and some designs are worlds apart from each other. Understanding the different types of car engines is essential for both novice car enthusiasts and experienced drivers.
In this article, delve into the world of automotive engines, from traditional internal combustion engines to cutting-edge electric propulsion.
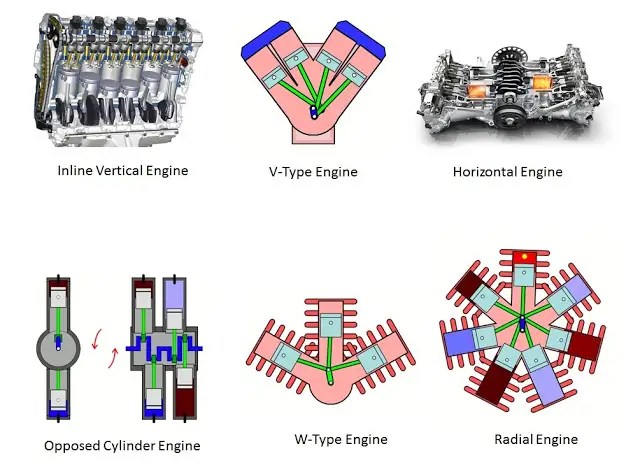
Inline Vertical Engine
- An inline engine is a very simple and traditional engine design. In the inline engine, the cylinders are installed in a single straight row. Therefore, it is also known as a straight engine, or I engine.
V Engine
- An engine that has 2 rows of cylinders angled less than 180 degrees between them and typically drives a common crankshaft that is inverted or upright.
Horizontal Engine
- This engine has two cylinder rows angled at 180 degrees. All of these cylinders drive a common crankshaft installed almost universally as a horizontal cylinder’s rows for aircraft or a vertically mounted crankshaft for helicopters.
Opposed cylinder Engine
- An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and factories.
W-Type Engines
- A W engine is a type of piston engine where three or four cylinder banks use the same crankshaft, resembling the letter W when viewed from the front.
Radial Engines
- A radial engine works like any other four-stroke internal combustion engine. Each cylinder has an intake, compression, power and exhaust stroke. They differ from inline and horizontally opposed engines in their firing order and they way they connect to the crankshaft.



Leave a comment