The fuel system is made up of the fuel tank, pump, filter and injectors or carburetor, and is responsible for delivering fuel to the engine as needed.
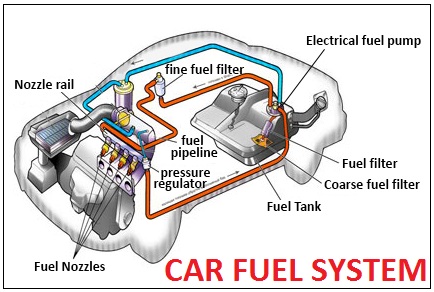
The function of the fuel system is to store and supply fuel to the cylinder chamber where it can be mixed with air, vaporized, and burned to produce energy. The fuel, which can be either gasoline or diesel is stored in a fuel tank. A fuel pump draws the fuel from the tank through fuel lines and delivers it through a fuel filter to either a carburetor or fuel injector, then delivered to the cylinder chamber for combustion.
Components
1. Fuel Tank : The fuel tank is the main storage for the fuel that runs the vehicle. Generally speaking, the gas tank is generally found at, or under, the rear of the vehicle.
2. Fuel Injectors : The fuel injectors are driven by the fuel pump and their job is to spray a fuel and air mixture into the combustion chamber, ready to be ignited to produce power to the driven wheels. The fuel injectors are basically a nozzle, with a valve attached, the nozzle creates a spray of fuel and air droplets (atomization). This can be viewed similar to that of a perfume dispenser or deodorant can in principle, spraying a fine mist.
3. Fuel Fill Hose : The Fuel Fill Hose is the main connector from the gas cap to the fuel tank. This is the point where the Gasoline (or other fuel) is put into the vehicle.
4. Gas Cap : The gas cap seals the fill hose and is used to ensure that :- Gas does not spill out from the car that the fuel system remains pressurized correctly in vehicles that use pressurized systems.
5. Fuel Pump : The fuel pump is used to pump the fuel from the fuel tank, via the fuel lines into the fuel injectors, which spray the fuel into the combustion chamber- in order to create combustion.
There are two types of fuel pump i.e mechanical fuel pumps (used in carburetors) and electronic fuel pumps (used in electronic fuel injection):-
• Mechanical fuel pumps: These are driven normally by auxiliary belts or chains from the engine.
• Electronic fuel pumps: Controlled by the Electronic Fuel Injection System, these are normally more reliable and have fewer reliability issues than their mechanical counterparts.
6. Fuel Filter : The fuel filter is the key to a properly functioning fuel delivery system. Fuel injectors are more susceptible to damage from dirt because of their close tolerances, but also fuel injected cars use electric fuel pumps. When the filter clogs, the electric fuel pump works so hard to push past the filter, that it burns itself up.
7. Fuel Lines : The Fuel Lines connect all of the various Fuel System components.
Steel lines and flexible hoses carry the fuel from the tank to the engine. When servicing or replacing the steel lines, copper or aluminum must never be used. Steel lines must be replaced with steel. When replacing flexible rubber hoses, the proper hose must be used. Ordinary rubber such as used in vacuum or water hose will soften and deteriorate. Be careful to route all hoses away from the exhaust system.
8. Fuel Gauge : The fuel gauge exists as a display item in the vehicle’s dashboard. It is intended to show to the driver the actual amount of fuel in the fuel tank. On older cars, it’s common for fuel gauges (or their related part, the sending unit) to be inaccurate. When you first start driving your classic car take time to learn how accurate the system is. It’ll save you from a long walk to the gas station if you run out of gas!
9. Fuel return lines : They are generally the same types of line tubing as the main Fuel Line. They are used to return excess fuel to the gas tank for recirculation and they capture gasoline vapors, which pushed back to the gas tank cool and condense back into the liquid. In particular, diesel-powered fuel injected engines often use the fuel as a cooling mechanism for the fuel injector. They can recirculate significant amounts of fuel.
10. Emission Vapor Controls : These are often used in combination with fuel return lines. The goal of this section of the overall system is to ensure that gasoline vapors are not released into the ambient air. If this occurs a number of bad things may happen:
1) The earth-shattering kaboom of gasoline vapors igniting.
2) The unpleasant smell of gasoline is routed into the interior of the vehicle.
3) It can harm the environment.



Leave a comment