The car braking system is a vital and sophisticated arrangement of various components working together to effectively slow down and stop the vehicle when required. It accomplishes this by converting the car’s kinetic energy into heat energy, which is then dissipated to reduce the car’s speed or bring it to a complete stop.
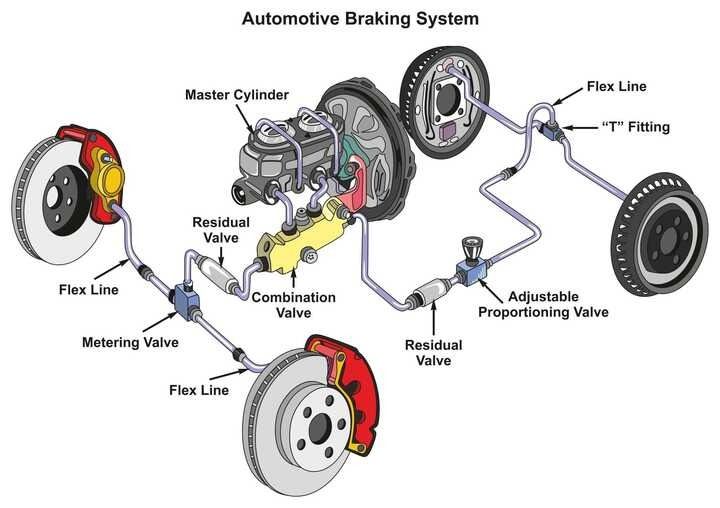
COMPONENTS USED IN BRAKING SYSTEM
- Brake Pedal: This component, located between the accelerator and clutch pedals inside the vehicle, is pressed by the foot to activate the brakes.
- Fluid Reservoir: The fluid reservoir houses the brake fluid or brake oil used in the braking system.
- Fluid Lines: Fluid lines consist of pipes through which brake fluid circulates within the vehicle.
- Brake Pads: Employed in disc brakes, brake pads are steel backing plates often composed of materials like ceramic, metal, or durable composites.
- Brake Shoes: Brake shoes are composed of two connected pieces of sheet steel that support the brake lining.
- Brake Drum: A rotating drum-shaped component integral to the drum brake system.
- Rotor: The rotor, often made of cast iron or reinforced materials like carbon-carbon or ceramics, serves as a brake disc connected to a wheel or axle.
- Brake Lining: Encased within the brake shoe, brake lining is a heat-resistant material with high friction properties, offering a balance of softness and toughness.
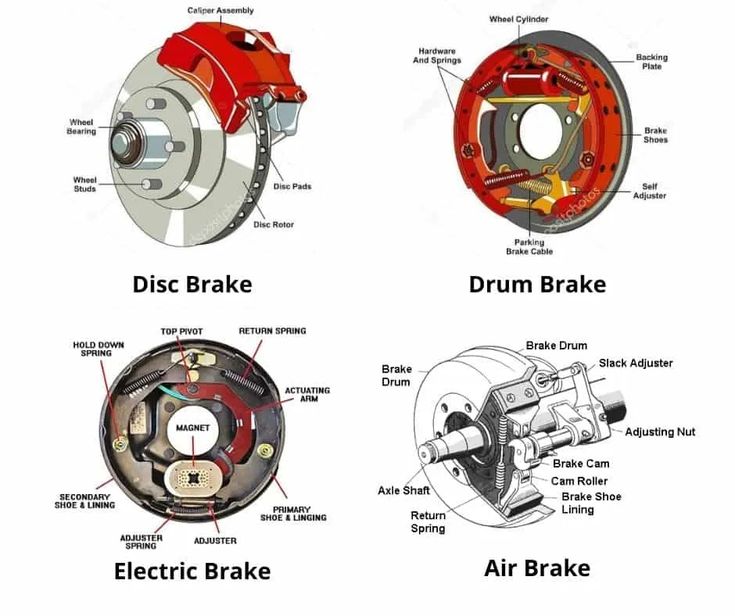
- Disc Brake:-
Brake rotors of disc brakes rotate with the wheels, and brake pads, which are fitted to the brake calipers, clamp on these rotors to stop or decelerate the wheels. The brake pads pushing against the rotors generate friction, which transforms kinetic energy into a thermal energy.
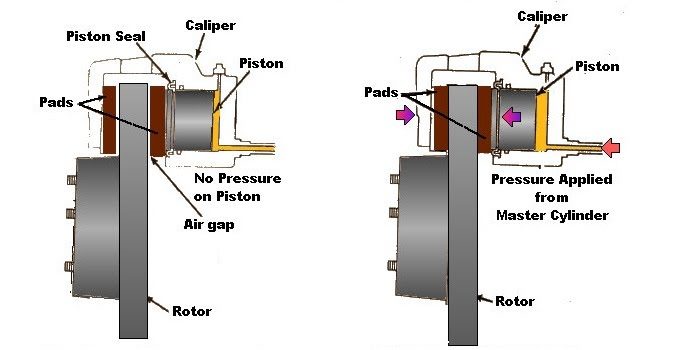
This thermal energy generates heat, but since the main components are exposed to the atmosphere, this heat can be diffused efficiently. This heat-dissipating property reduces brake fade, which is the phenomenon where braking performance is influenced by the heat. Another advantage of disc brake is its resistance to water fade, which occurs when the water on the brakes significantly reduces braking force. When the vehicle is in motion, the rotor spins at high speeds and this rotational motion discharges the water from the rotors themselves, resulting in stable braking force.
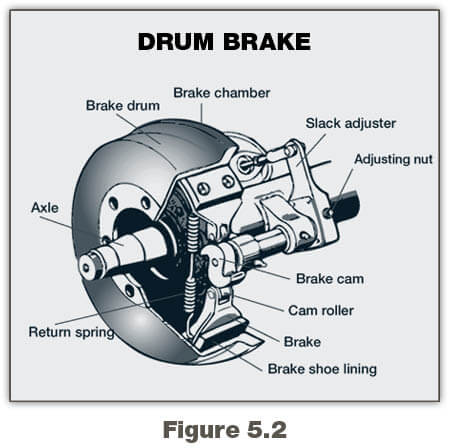
2. Drum Brake:-
A drum brake is a type of mechanical braking system commonly used in vehicles to slow down or stop their motion. This braking mechanism operates through the interaction of friction between brake shoes and the inner surface of a drum-like component attached to the wheel. Drum brakes have a long history and are still found in various automotive applications, though they have become less common in newer vehicles due to the emergence of more advanced disc brake systems.
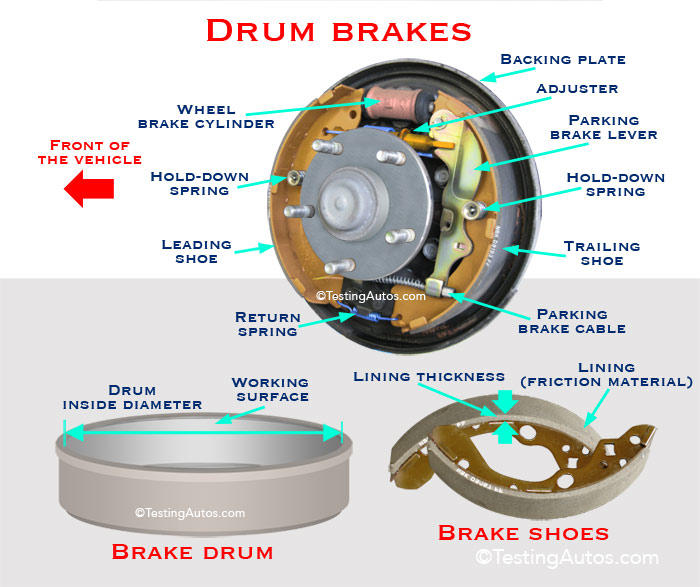
When the shoes press against the outer surface of the drum, this configuration is often referred to as a clasp brake. In cases where the drum gets pinched between two shoes—similar to the setup in a conventional disc brake—it might be referred to as a pinch drum brake, although such brake setups are relatively uncommon. Another related type, known as a band brake, employs a flexible belt or “band” that wraps around the exterior of a drum. Drum brakes are primarily applied at the rear axle of small and compact vehicles.
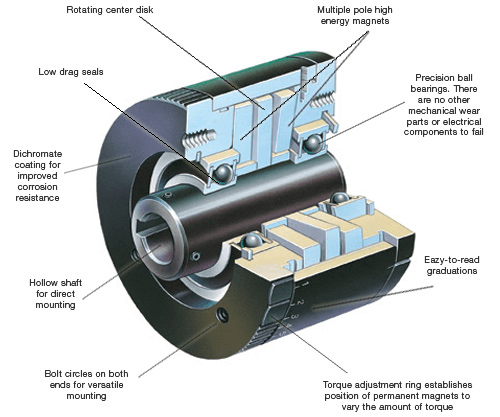
3. Electric Brake:-
Electric brakes are devices that use an electrical current or magnetic actuating force to slow or stop the motion of a rotating component. They are used in industrial and vehicular braking applications that require fast response times and precise tension control.
4. Air brake:-
Air brakes operate using compressed air to control and facilitate the braking process in heavy vehicles. The system comprises several key components, including an air compressor, reservoir tanks, valves, hoses, brake chambers and brake shoes or pads.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, compressed air stored in the reservoir tanks is released through valves and hoses to the brake chambers. This release of air pressure activates the brakes, causing the brake shoes or pads to engage with the drums or rotors, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle.



Leave a comment